MUMPS Main Features
-
Solution of large linear systems with
symmetric positive definite matrices
general symmetric matrices
general unsymmetric matrices - Real or complex arithmetic (single or double precision)
-
Parallel factorization and solve phases
(uniprocessor version also available) - Out of core numerical phases
- Iterative refinement and backward error analysis
-
Various matrix input formats
assembled, distributed, elemental format
- Partial factorization and Schur complement matrix (centralized or 2D block-cyclic) with reduced/condensed right-hand side
- Interfaces to MUMPS: Fortran, C, Matlab and Scilab
- Several reorderings interfaced: AMD, QAMD, AMF, PORD, METIS, PARMETIS, SCOTCH, PT-SCOTCH
-
Symmetric indefinite matrices:
preprocesssing and 2-by-2 pivots
- Parallel analysis and matrix scaling
- Computation of the determinant (with an option to discard factors)
- Forward elimination during factorization
Recent features
- Detection of null pivots, null space basis estimate
- Sparse multiple right-hand side, distributed solution; Exploitation of sparsity in the right-hand sides
- Computation of selected entries in the inverse of a matrix
- Block Low Rank (BLR) factorization and solve
- Selective 64-bit integer feature for matrices with more than 2 billion nonzeros
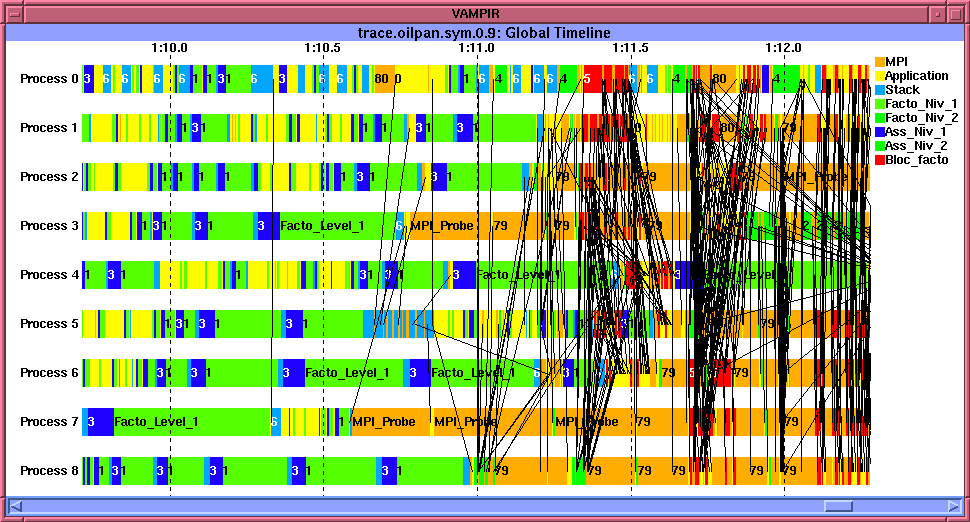
A fully asynchronous distributed solver (VAMPIR trace)
Implementation
- Distributed Multifrontal Solver (Fortran 95, MPI) using shared-memory parallelism (OpenMP, multithreaded BLAS) within each MPI process;
- Dynamic Distributed Scheduling to accomodate numerical fill-in, load balancing and multi-user environment;
- Use of BLAS, BLACS, ScaLAPACK.
Partially funded by CEC ESPRIT IV long-term research project
-- No. 20160 (PARASOL)
